OXIGEN salud
Oxygen therapy

OXIGEN salud
Oxygen therapy
This involves administering oxygen at a higher concentration than the oxygen in the air around us (21 %) to treat hypoxia or a lack of oxygen in the body’s tissues. Long-term oxygen therapy is completely different to oxygen therapy in an acute setting. The first can be administered at home, while the second takes place when the patient is hospitalised.
There are different oxygen delivery systems available for oxygen therapy. The prescribing clinician will determine the type of system and accessories to use, the oxygen flow rate and the treatment time. All of these systems administer oxygen through a mask or a nasal cannula. OXIGEN salud brings the equipment and the consumables prescribed to the patient’s home.
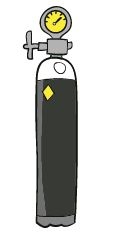
This is the traditional system for supplying oxygen at home, using high-pressure steel cylinders. OXIGEN salud can adapt the supply frequency to the patient’s needs.
Currently, oxygen cylinders are only used as an emergency system, when there is a fault with the usual oxygen source or the electricity supply, when the usual oxygen source is empty, or when the liquid oxygen system is not enough.
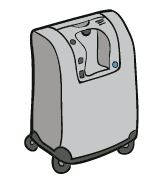
These are electrical medical devices that separate oxygen from the air. They can be stationary (home concentrator) or portable, the latter providing greater freedom and movement for the patient.
OXIGEN salud works with the most reputable concentrator manufacturers and carries out regular checks on all equipment.
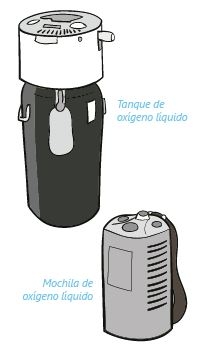
Large quantities of oxygen can be stored when it is kept at low temperatures. Before being administered to the patient, medical liquid oxygen is warmed up to room temperature inside the system and vaporises into a gas. OXIGEN salud can provide this system in a stationary cryogenic container and a refillable portable unit, which gives the patient more mobility.
| Source | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen cylinder | Low cost | Limited mobility Heavy Frequent replacement |
| Home oxygen concentrator | Low cost Mobile Easy to use Long-lasting |
Electricity consumption Noise Regular checks |
| Portable oxygen concentrator | Lightweight Small size Can be charged anywhere (even in a car) Accepted on flights Pulse-flow option (1–6 pulses) Continuous-flow option |
Not very effective at high flow rates Can not usually exceed 3–5 l/min |
| Liquid oxygen | No noise No electricity consumption High flow rates |
Evaporation Heavy weight Frequent replacement |
| Liquid oxygen backpack | Lightweight Small size Lasts 4–8 hours depending on the flow rate Pulse-flow option (1.5–5 pulses) Continuous-flow option |
Expensive |
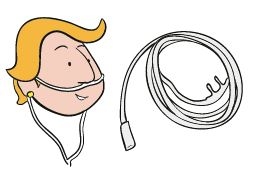
This device consists of a plastic cannula with two prongs that fit into the nostrils, hook around the ears and come together under the chin. This is the most comfortable and commonly used method, as it allows the patient to eat, drink, expectorate and speak without needing to take it off.
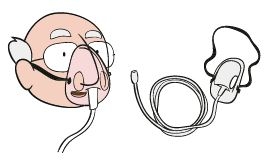
This device covers the face from the nose to the chin and has holes in the sides so that the exhaled air can be expelled. It allows for higher concentrations of oxygen than the nasal cannula. However, it can be uncomfortable, as it interferes with eating and washing, and it may move during sleep.
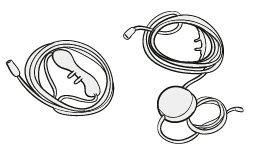
Unlike the ordinary nasal cannula, this device is used with a continuous-flow system and is useful when a high flow rate is needed. It is rarely used in day-to-day clinical practice.
Calculate the autonomy of your oxygen bottle
Shall we call you?