OXIGEN salud
Mechanical ventilation
OXIGEN salud
Mechanical ventilation
Non-invasive mechanical ventilation (NIMV) is a type of respiratory support that helps the patient breathe using a positive pressure ventilator, through an interface and without the need for an artificial airway such as a tracheostomy.
The interfaces are designed to fit comfortably against the face and allow for the efficient delivery of pressurized air. The most common ones include:
Today, the variety of standard masks available offers high adaptability and comfort, avoiding the need for custom-made devices in most cases.
NIV offers significant benefits compared to other invasive methods, although it may also have certain limitations.
Choosing the right type of mask is crucial, both for fit and ventilation effectiveness. It's important that it:
The nasal mask offers several advantages, including ease of use, reduced claustrophobia, the ability for the patient to expectorate without removing the mask, and fewer potential complications in case of vomiting. Furthermore, its small size creates minimal dead space.
However, a significant problem is leakage due to poor sealing of the interface, which must be prevented with a secure fit using a cap or harness, or leakage from the mouth, which can sometimes be resolved by using a chin strap or oronasal mask.
The oronasal or full-face mask, by covering the nose and mouth, prevents oral leakage in patients who breathe through their mouths. It also allows for higher pressure support with less leakage and requires less cooperation from the patient.
The disadvantages of the full-face mask are that it is more uncomfortable and bulky, which can cause claustrophobia, and it creates more dead space. Furthermore, it can sometimes cause leaks if the mask is not properly fitted to the patient's facial anatomy.
The mouthpiece facilitates communication and clearance of secretions. However, adverse effects have been described, such as dry mouth, an increased risk of aspiration, altered dental occlusion, and temporomandibular joint problems. They are especially useful in situations of high ventilator dependence. However, they can hardly be tolerated for more than 16 hours per day.
To carry out this treatment it is necessary:
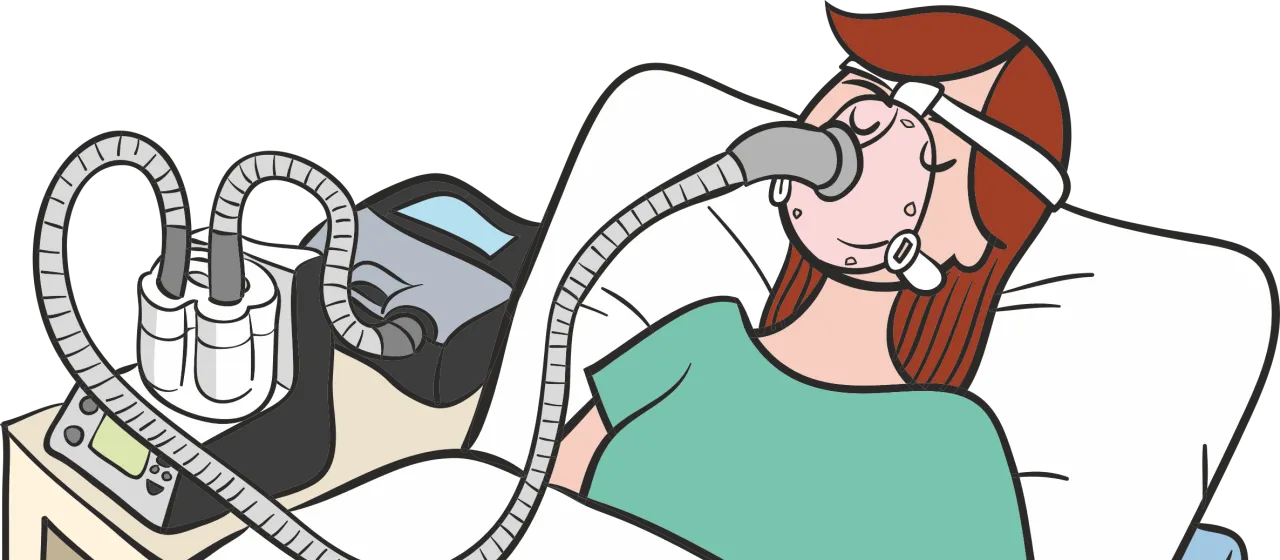
a. The ventilator, which generates airflow at a specific pressure.
b. The tubing, the piece that connects the ventilator to the patient.
c. The air humidifier, which is optional, is placed at the ventilator's air outlet and helps prevent dryness of the mucous membranes.
d. An interface (nasal mask, prongs, mouthpiece, face mask, or full-face mask) that connects the patient to the ventilator. Different types and varieties of interfaces are available to achieve better adaptation to the ventilator.
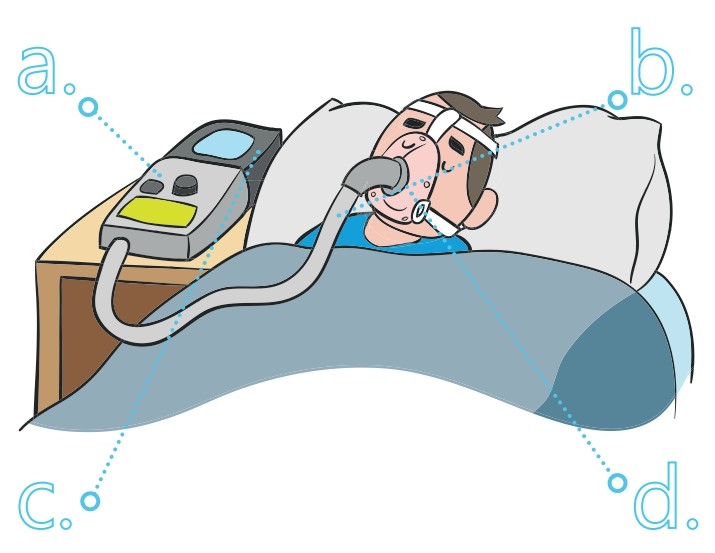
Place the ventilator on a bedside table, near the headboard, so that it cannot fall over during sleep. Make sure you do not place the machine somewhere where someone might bump into it or trip on its power cable.
Ensure the area around the machine is clean and dry. The machine should be positioned so that nothing is obstructing the air inlet found at the back of the ventilator. Connect one end of the power cable to the ventilator and plug the other into the mains.
A light will come on to indicate that the ventilator is plugged in.* Connect the tubing to the interface (and to the humidifier if this has been prescribed).
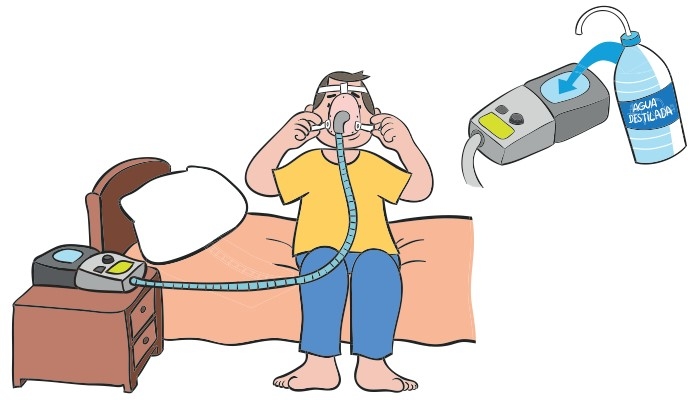
The treatment may be more comfortable for the patient if a humidifier is used to humidify the air they are breathing. The humidifier tank, which is attached to the ventilator, must be filled with distilled water up to the corresponding line.
Every time the ventilator is moved, first, the remaining water must be emptied, and then, the humidifier must be disconnected.
* This depends on the model of the machine. Check the instruction manual.
There are two types of masks:

Nasal mask

Outdoor mask

Unfasten the bottom clip on the headgear, hold the mask over your nose and pull the headgear over your head. Make sure the straps are not twisted.
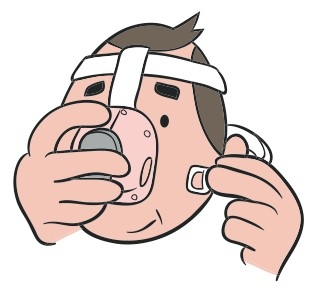
Fasten the bottom clip again and make sure it is secure.

Adjust the upper straps so that they are even. Make sure they are not too tight. Adjust the lower straps until they are comfortable.
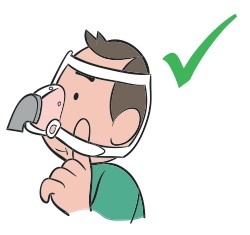
Connect one end of the tubing to the mask and the other end to the ventilator.

Turn the machine on and breathe normally.

Adjust the straps to correct any leaks.
Lie down and adjust the tubing so that you can move freely if you turn over while you sleep.
There is no need to alter the headgear on the mask provided by OXIGEN salud every time you use it. The care team will fit it to your head when they install the machine.
The care team of OXIGEN salud will carry out regular checks on the equipment. However, it is important to follow the hygiene and cleaning guidelines described below, as they will make the treatment more comfortable and ensure the machine lasts as long as possible.

Before going to bed, wash your face. This will remove any excess oil before you put the mask on.
Wash the mask daily with water and mild soap. Rinse it thoroughly and leave it to dry. Store it in a clean, dry place.
The headgear can be washed with laundry in the washing machine.
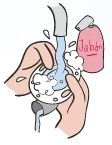
The tubing should be washed with warm water and mild soap. Rinse it thoroughly then hang it up to dry (not outside, as the plastic might get damaged). Store it in a clean, dry place.
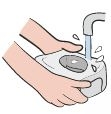
The humidifier should be washed with warm water and mild soap. Rinse it well and fill it with distilled water. The water in the tank should be changed at least every two days.
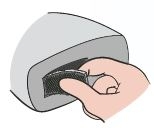
Remove the air filter from the ventilator and clean it regularly.
Unplug the ventilator and clean it regularly with a slightly damp cloth. Do not submerge the machine or its power cable in water. Always unplug the machine before cleaning it. Make sure it is dry before you plug it back in.
If the patient needs to travel, they can do so without any problems. They must always notify OXIGEN salud and follow their airline’s guidelines.
Shall we call you?